-
 The rapid development of biomaterials and biotechnology has provided important means for revealing life phenomena and life processes, which is the basis for tissue and organ regeneration and reconstruction, and so is the catalyst for a second life. This special issue “Development and Exploration of Biomaterials in Shenzhen” has published wonderful reports and extended content of the 2021 Shenzhen Biomedical Materials Annual Conference, so that the readers who were unable to attend due to the COVID-19 epidemic could also take a glimpse of this annual conference via the special issue. [MORE]
The rapid development of biomaterials and biotechnology has provided important means for revealing life phenomena and life processes, which is the basis for tissue and organ regeneration and reconstruction, and so is the catalyst for a second life. This special issue “Development and Exploration of Biomaterials in Shenzhen” has published wonderful reports and extended content of the 2021 Shenzhen Biomedical Materials Annual Conference, so that the readers who were unable to attend due to the COVID-19 epidemic could also take a glimpse of this annual conference via the special issue. [MORE] -
 The ocean plays an important role in the future development. The Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology(SIAT), Chinese Academy of Sciences has deeply involved in the field of marine science. This special issue introduces recent research of SIAT’s team, covering marine engineering technology, underwater acoustic technology, underwater wireless transmission technology, marine biochemical sensing technology and seawater desalination technology, etc. In addition, low-power marine instrument recovery communication beacons developed by Professor Yang Ting’s team [MORE]
The ocean plays an important role in the future development. The Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology(SIAT), Chinese Academy of Sciences has deeply involved in the field of marine science. This special issue introduces recent research of SIAT’s team, covering marine engineering technology, underwater acoustic technology, underwater wireless transmission technology, marine biochemical sensing technology and seawater desalination technology, etc. In addition, low-power marine instrument recovery communication beacons developed by Professor Yang Ting’s team [MORE] -
 Advanced electronic material is one of the three main elements of integrated circuit and is the foundation and support of electronic information industry. Trade frictions occurred in recent years fully illustrate the strategic importance of materials, especially electronic materials used in integrated circuit industry. In this context, we specially invited Professor Rong Sun, director of the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Electronic Materials, as the guest editor to organize the special issue focused on high-end electronic packaging materials for integrated circuit [MORE]
Advanced electronic material is one of the three main elements of integrated circuit and is the foundation and support of electronic information industry. Trade frictions occurred in recent years fully illustrate the strategic importance of materials, especially electronic materials used in integrated circuit industry. In this context, we specially invited Professor Rong Sun, director of the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Electronic Materials, as the guest editor to organize the special issue focused on high-end electronic packaging materials for integrated circuit [MORE] -
 In recent years, the Chinese government has provided strong support for new energy vehicles and intelligent connected vehicles in terms of scientific and technological research, industrial development, application demonstration, and market promotion. Interestingly, China has become one of the most active countries in the field of new energy vehicles. Although the new energy vehicle industry has shown a good momentum in China, it has to overcome core technological barriers. [MORE]
In recent years, the Chinese government has provided strong support for new energy vehicles and intelligent connected vehicles in terms of scientific and technological research, industrial development, application demonstration, and market promotion. Interestingly, China has become one of the most active countries in the field of new energy vehicles. Although the new energy vehicle industry has shown a good momentum in China, it has to overcome core technological barriers. [MORE] -
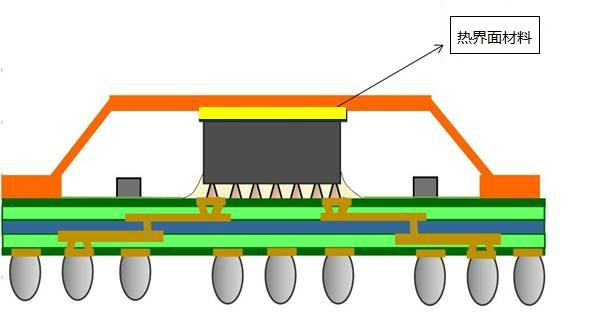 With the rise of 5G communication, Internet of Things, new energy automotive electronics, wearable devices, and smart cities, affiliated electronic devices are developing towards the directions of miniaturization, high-power density, and multi-functionality. This will continue to increase the risk of overheating with related electronic devices. The development of high-performance thermal management materials is crucial to improve the heat dissipation of electronic devices, and it has become the biggest challenge faced by academia and application industry in electronic devices. [MORE]
With the rise of 5G communication, Internet of Things, new energy automotive electronics, wearable devices, and smart cities, affiliated electronic devices are developing towards the directions of miniaturization, high-power density, and multi-functionality. This will continue to increase the risk of overheating with related electronic devices. The development of high-performance thermal management materials is crucial to improve the heat dissipation of electronic devices, and it has become the biggest challenge faced by academia and application industry in electronic devices. [MORE] -
 Recently, with the maturity and popularization of technologies such as Internet of Things, cloud computing, mobile internet, and Internet of Vehicles, massive data in various formats like images, audiovisual materials, and health files are rapidly generated. The International Data Corporation (IDC) predicted that global data volume would reach 175 ZB (approximately 175 billion TB) by 2025, which indicated that more than 99% of all data in human civilization were generated in recent years. [MORE]
Recently, with the maturity and popularization of technologies such as Internet of Things, cloud computing, mobile internet, and Internet of Vehicles, massive data in various formats like images, audiovisual materials, and health files are rapidly generated. The International Data Corporation (IDC) predicted that global data volume would reach 175 ZB (approximately 175 billion TB) by 2025, which indicated that more than 99% of all data in human civilization were generated in recent years. [MORE] -
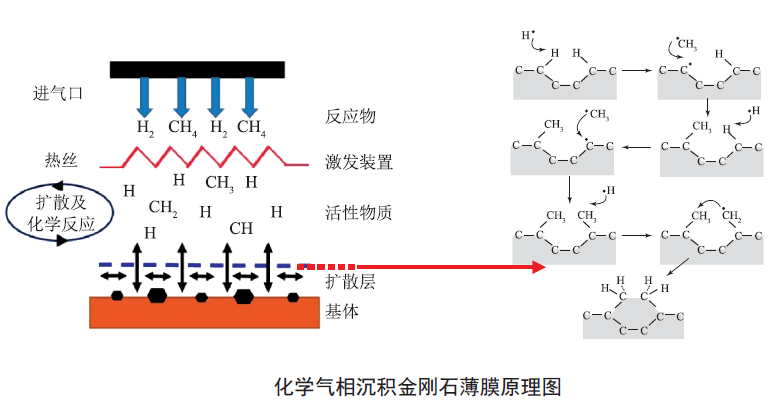 This special issue majorly reports the research exploration made by the key members from Guangdong Innovation Team of Advanced Functional Film Materials and Industrial Applications, which includes the analysis and discussion of preparation methods and growth mechanism of high-preferred orientation diamond film and high-quality single crystal diamond, the research of diamond film in cemented carbide tools, the latest research progress on film thermal expansion coefficient and residual stress testing technology. [MORE]
This special issue majorly reports the research exploration made by the key members from Guangdong Innovation Team of Advanced Functional Film Materials and Industrial Applications, which includes the analysis and discussion of preparation methods and growth mechanism of high-preferred orientation diamond film and high-quality single crystal diamond, the research of diamond film in cemented carbide tools, the latest research progress on film thermal expansion coefficient and residual stress testing technology. [MORE] -
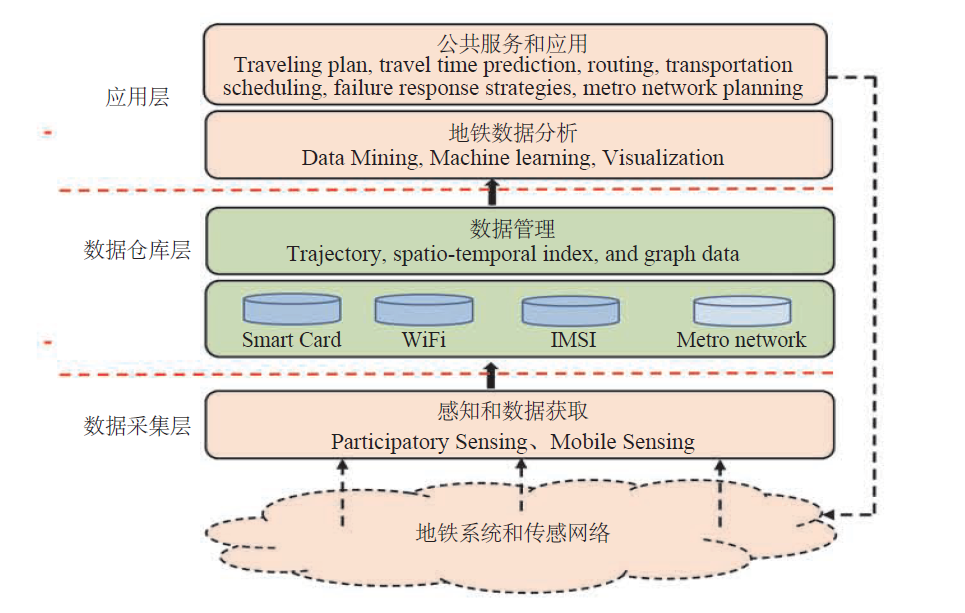
 Big data is leading a new round of technological innovation, and it has brought new impetus and opportunities for the transformation and upgrading of social economy and the enhancement of national competitiveness. Therefore, many countries have proposed initiatives to develop big data. In recent years, big data has triggered extensive studies in a variety of disciplines and brought changes in terms of technology, model and ideology to different industries. The special issue was organized around big data platforms and supporting technologies, and big data applications, security and privacy [MORE]
Big data is leading a new round of technological innovation, and it has brought new impetus and opportunities for the transformation and upgrading of social economy and the enhancement of national competitiveness. Therefore, many countries have proposed initiatives to develop big data. In recent years, big data has triggered extensive studies in a variety of disciplines and brought changes in terms of technology, model and ideology to different industries. The special issue was organized around big data platforms and supporting technologies, and big data applications, security and privacy [MORE] -
 Intelligent connected vehicles are equipped with advanced on-board sensors, controllers, actuators and other devices, and integrate modern communication and network technologies to realize information sharing between vehicles, roads, people, and clouds to achieve "safe, efficient, comfortable and energy-saving" driving. Although the industry shows a positive trend of comprehensive development, it is facing several technical adjustments on core technology level, including bicycle perception and decision-making, vehicle-road cooperation, human-machine co-driving [MORE]
Intelligent connected vehicles are equipped with advanced on-board sensors, controllers, actuators and other devices, and integrate modern communication and network technologies to realize information sharing between vehicles, roads, people, and clouds to achieve "safe, efficient, comfortable and energy-saving" driving. Although the industry shows a positive trend of comprehensive development, it is facing several technical adjustments on core technology level, including bicycle perception and decision-making, vehicle-road cooperation, human-machine co-driving [MORE]

- Current Issue
- In Press
- Archive
- Virtual Special Issue
- Most Downloaded
- Most Cited
-
ZHANG Jiashuai, YANG Liuqing, FU Qilin, CHENG Huiwu, SHAO Cuiping, LI Huiyun
2025,14(3):1-23 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20240914001 ,CSTR: 32239.14.j.issn.2095-3135.20240914001
Abstract:
Chiplet-based multi-chip integration designs provide a flexible and scalable solution that surpasses traditional system on chip monolithic integration. However, inter-Chiplet communication has become a significant bottleneck affecting overall system performance. The network on interposer plays a pivotal role in multi-chip systems, directly influencing both performance and development costs. This paper reviews the communication topologies of Chiplet-based network on interposer structures and delves into the design and implementation methods of current inter-Chiplet communication architectures. It comprehensively covers the communication process from protocol, interface, to application layers, classifying interconnect topologies based on structural configurations, and providing in-depth analyses and cross-comparisons for each category. Additionally, this paper explores the future directions of inter-Chiplet communication technologies, emphasizing technical challenges and potential solutions, and highlights the importance of workload-oriented, reusable interposer layers and topology design. This review aims to provide researchers with a comprehensive overview of the current state of network on interposer technology while simultaneously forecasting its development trends in future multi-chip integrated systems, offering systematic insights to advance frontier research in semiconductor technologies.
-
LIANG Zhanxiong, SUN Xudong, CAI Yongda, ZHANG Yuming, MAI Langjie, HE Yulin, HUANG Zhexue
2025,14(3):24-37 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20240224001 ,CSTR: 32239.14.j.issn.2095-3135.20240224001
Abstract:
Unlike the popular MapReduce computing framework, LOGO is a new distributed computing framework using a LOcal-GlObal computing paradigm. Under the LOGO framework, big data distributed computing is completed in two steps. The LO operation runs a serial algorithm in a number of slave nodes or virtual machines to process independently the random sample data blocks, generating local results. The GO operation uploads all local results to the master node and integrate them to obtain the approximate result of the big data set. The LOGO computing framework eliminates data communication between nodes during iterations of the algorithm, greatly improving computing efficiency, reducing memory requirements, and enhancing data scalability. This article proposes a new distributed machine learning algorithm library under the LOGO computing framework. A new distributed computing is divided into two parts: the serial algorithm executed by the LO operation and the ensemble algorithm executed in the GO operation. The LO operation can directly execute existing serial machine learning algorithms without the need to rewrite them according to MapReduce. The GO operation executes ensemble algorithms of different kinds depending on the ensemble tasks. In this article, the principle of LOGO distributed computing is introduced first, followed by the algorithm library structure, the method for packaging existing serial algorithms and the ensemble strategy. Finally, implementation in Spark, App development, and the results of performance tests for various algorithms are demonstrated.
-
2025,14(3):38-50 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20240612001 ,CSTR: 32239.14.j.issn.2095-3135.20240612001
Abstract:
In the era of big data, the storage of massive amounts of data has become a challenging problem. DNA storage technology, as a cutting-edge solution to this challenge, particularly focuses on the development and challenges of information editing technology. Initially, DNA storage primarily served “cold” data, but the latest advancements in the technology have driven its development towards supporting data updates and management for more advanced applications. This paper proposes an incremental management method for secure DNA storage, designing a hybrid encryption mechanism that supports multi-party editing and a DNA incremental storage model. While ensuring security, this model achieves secure and efficient information editing and management under existing technological constraints through a partitioned storage scheme and efficient indexing encoding. This approach meets the modern data management requirements for flexibility and cost-effectiveness, providing new perspectives and strategies for addressing core issues in DNA data management.
-
2025,14(3):51-63 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241201003 ,CSTR: 32239.14.j.issn.2095-3135.20241201003
Abstract:
Existing indoor three-dimensional (3D) object detection is able to detect a limited number of object categories, thus limiting the application on intelligent robotics. Open-vocabulary object detection is able to detect all objects of interest in a given scene without defining object categories, thus solving the shortcomings of indoor 3D object detection. At the same time, the large language model with prior knowledge can significantly improve the performance of visual tasks. However, existing researches on open-vocabulary indoor 3D object detection only focuses on object information and ignores contextual information. The input data for indoor 3D object detection is mainly point cloud, which suffers from sparsity and noise problems. Relying only on the object point cloud can negatively affect the 3D detection results. Contextual information contains scene information, which can complement the object information to promote the recognition on object category. For this reason, this paper proposes an open-vocabulary 3D object detection algorithm based on contextual information assistance. The algorithm integrates contextual information and object information through a large language model, and then performs chain-of-thought reasoning. The proposed algorithm is validated on SUN RGB-D and ScanNetV2 datasets, and the experimental results show the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
-
DOU Mingyang, GENG Yanjuan, YANG Jiabin
2025,14(3):64-77 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241030001 ,CSTR: 32239.14.j.issn.2095-3135.20241030001
Abstract:
Hand pose estimation based on RGB images holds wide application prospects in dynamic gesture recognition and human-computer interaction. However, existing methods face challenges such as high hand self-similarity and densely distributed keypoints, making it difficult to achieve high-precision predictions with low computational costs, thereby limiting their performance in complex scenarios. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a 2D hand pose estimation model named FAR-HandNet, based on the YOLOv8 network. The model ingeniously integrates a focused linear attention module, a keypoint alignment strategy, and a regression residual fitting module, effectively enhancing feature capture capabilities for small target regions (e.g., hands) while mitigating the adverse effects of self-similarity on the localization accuracy of hand keypoints. Additionally, the regression residual fitting module leverages a flow-based generative model to fit the residual distribution of keypoints, significantly improving regression precision. Experiments were conducted on the Carnegie Mellon University panorama dataset (CMU) and the FreiHAND dataset. Results demonstrate that FAR-HandNet exhibits remarkable advantages in parameter size and computational efficiency. Compared to existing methods, it achieves superior performance in the percentage of correct keypoints under varying thresholds. Furthermore, the model achieves an inference time of only 32 ms. Ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of each module, conclusively verifying the efficacy and superiority of FAR-HandNet in hand pose estimation tasks.
-
LI Yisheng, XU Yongjie, WANG Shuqiang, WANG Yishan
2025,14(3):78-86 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241127001 ,CSTR: 32239.14.j.issn.2095-3135.20241127001
Abstract:
With the rapid development of deep learning technology, autism screening based on neural signals such as electroencephalography (EEG) is gradually emerging as a novel diagnostic approach. However, due to the complexity of EEG data acquisition, especially for children, insufficient data often poses a challenge. Data augmentation methods are commonly used to address the scarcity of real-world data, with generative adversarial networks (GANs) being a frequently applied technique. However, due to the limited scale and diversity of data, current augmentation methods have not yet to achieve optimal classification performance. This study introduces an improved conditional diffusion model to enhance both raw EEG signals and their corresponding functional connectivity temporal graphs. Experimental results demonstrate that this method significantly improves autism classification performance, achieving maximum classification accuracies of 84.38% and 79.01% for resting-state and task-state data, respectively. These findings validate the effectiveness of data augmentation based on the conditional diffusion model in enhancing autism screening outcomes.
-
DAI Wei, ZHANG Haoxuan, CHEN Fangxu, PENG Wei
2025,14(3):87-101 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241012001 ,CSTR: 32239.14.j.issn.2095-3135.20241012001
Abstract:
Cancer is a genetically related disease with multiple subtypes, each exhibiting significant differences in genetics, phenotype, and treatment response. Accurate classification of cancer subtypes is critical for personalized treatment, as it helps improve therapeutic outcomes. However, cancer subtype classification methods based on patient gene expression data often struggle to effectively distinguish rare subtypes in the presence of imbalanced samples. To address this issue, a cancer subtype classification method called MFP-VAE (meta-learning few-shot prototype learning VAE) is proposed, focusing on handling datasets with imbalanced samples. This method improves the sampling strategy to ensure balanced consideration of different subtypes in meta-learning tasks. The model employs a variational autoencoder for feature extraction and classifies samples by calculating the distance between the samples and their corresponding cancer subtype prototypes. Experimental results show that MFP-VAE outperforms existing methods on two public cancer datasets, significantly improving classification performance, especially under imbalanced sample conditions. Furthermore, survival analysis reveals that the distinguished cancer subtypes exhibit significant differences in clinical characteristics.
-
LIU Gaocheng, TONG Jiabo, YANG Shilin, WANG Qiuying, TANG Xinyu, LIU Chang, LIU Jia
2025,14(3):102-118 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20250118001 ,CSTR: 32239.14.j.issn.2095-3135.20250118001
Abstract:
Cerebral blood flow velocity (CBFV) reconstruction plays a crucial role in evaluating cerebrovascular function, particularly in the early diagnosis of cerebrovascular diseases, optimizing treatment plans, and preventing strokes. Existing CBFV reconstruction methods face challenges in accuracy and efficiency when processing multivariate time-series signals, particularly in the context of data scarcity and complex signal processing. This study proposes a multivariate time-series model based on a Transformer encoder, which achieves high-precision CBFV reconstruction using arterial blood pressure and CO2 time-series signals. The model design is based on a long short-term memory module, which effectively compensates for the limitations of the global attention mechanisms in processing local information and enhances local feature learning. Additionally, a hybrid loss function is employed to optimize local waveform errors, improving reconstruction accuracy. Furthermore, to address the issue of data scarcity in the target domain, this study introduces a transfer learning strategy based on the correlation between arterial blood pressure and electrocardiogram signals, alleviating the impact of limited data on model performance. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms traditional regression and deep learning models in the CBFV reconstruction task, with a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.51870, a dynamic time warping distance of 17.879, and mutual information of 0.34375, while completing the reconstruction of 200 data points in 0.04 s. The study validates the effectiveness of this method in precision medicine and provides innovative solutions for clinical diagnosis, disease prevention, and personalized treatment, with broad application prospects, particularly in medical signal processing, intelligent healthcare, and health monitoring.
-
KANG Jianjun, NIE Junxi, JING Jialu, CHANG Yiting, ZHOU Wenqing, LIU Chaoran
2025,14(3):119-133 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20240828001 ,CSTR: 32239.14.j.issn.2095-3135.20240828001
Abstract:
This article introduces a ocean buoy data acquisition system based on modular design concept. The proposed system is divided into 3 modules according to the functions of ocean buoy data, i.e. the meteorological safety, hydrology biochemistry and communication. The device can realize continuous acquisition and processing of multiple devices of buoy, as well as real-time two-way communication and other functions. According to the characteristics of different modules, multiplexers and serial port expansion chips are used to realize the interface expansion of the system, which improves the carrying capacity of the system from the hardware. The communication module uses direct memory access technology to realize the forwarding, retransmission and remote control of dual-channel real-time data, realizes the reliable and safe operation of the buoy system at sea, and also improves its human-computer interaction function. The system has been tested in the laboratory and on-site operation experiments at sea to verify its stability, reliability and measurement accuracy.
-
JIANG Biao, ZHENG Jianglong, HUANG Xiaoxin, LI Zhifeng, LI Linwei, HUANG Yifan
2025,14(3):134-144 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241010001 ,CSTR: 32239.14.j.issn.2095-3135.20241010001
Abstract:
Electromagnetic pulse sound source (boomer) is a commonly used explosion sound source in marine seismic exploration, and the deep-sea application of such explosion sound source needs to solve cavitation suppression problem. In this paper, a deep sea boomer source based on pressure compensation balance is proposed. A boomer transducer with a maximum working pressure of 20.0 MPa is developed and tested in a high-pressure anechoic tank. Through the analysis of the hydrophone outputs under different energy and pressure levels, it can be seen that an air sac with the initial pressure of 0.5 MPa can effectively balance the internal and external pressure of the transducer, solve the problem of cavitation suppression, and realize the excitation of broadband pulse sound waves. The repeatability of the acoustic wave is very good, and the minimum correlation coefficient is to 0.986. With the increase of working pressure from 0.5 MPa to 20.0 MPa, the main change in acoustic characteristics is the amplitude attenuation (204.6 dB to 194.2 dB) and width compression (182 μs to 88 μs), and the main frequency (2.3 kHz as the center) slightly shifted to high frequency. Compared with the hydrophone output in the process of pressure rising and downing in the high-pressure anechoic tank, it can be seen that the repeatability of the acoustic wave is better. The higher the pressure, the better the waveform consistency, indicating that the boomer transducer based on pressure compensation balance has a more stable performance under high pressure environment.
-
ZHENG Jianglong, JIANG Biao, LI Zhifeng, HUANG Xiaoxin, LI Linwei, HUANG Yifan
2025,14(3):145-152 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241205001 ,CSTR: 32239.14.j.issn.2095-3135.20241205001
Abstract:
The high-pressure anechoic water tank is an important experimental testing platform for the development of deep-sea transducers, sensors, and other acoustic instruments and equipment. In this paper, background noise and acoustic field fluctuations at different frequencies were measured for the homemade 20 MPa high-pressure anechoic tank. The echo interference level under fixed measurement position and distance conditions was calculated, and the echo interference curve was drawn. The time-frequency characteristics of signals under typical low-frequency and high-frequency conditions were analysed. The measurement results of background noise show that although the background noise inside the tank is relatively high and has characteristic peaks in the frequency range of 10–12 kHz, it allows for measurement experiments with sufficient signal-to-noise ratio conditions. Meanwhile, the time-domain waveform results of sound field fluctuations measured in different frequencies show that the signal amplitude rapidly decays after a transmission width of 2 ms, and the higher the frequency, the faster the attenuation, indicating that the sound absorption cone inside the tank has a good sound absorption effect. The calculation results of echo interference level show that most frequency points above 10 kHz do not exceed ±1 dB. The designed fixed measurement position meets the requirements of free field testing, especially the echo interference of frequency points such as 20 kHz, 28 kHz, and 34 kHz does not exceed ±0.5 dB, which meets the requirements of precision measurement.
-
Chen Shuaibao,LIU Peng,HE Wei,TAN Yuguang,CHEN Liangpei,LUO Dong,JIAO Guohua,CHEN Wei
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20250106001
Abstract:
The selective absorption and scattering effects of water on visible light of different wavelengths severely constrain the quality of optical imaging. Polarization imaging technology demonstrates significant advantages in high-turbidity, short-range underwater environments. This study employs an active polarization imaging system utilizing three laser wavelengths—red, green, and blue—to comparatively analyze imaging performance in typical natural water with turbidity levels of 10-25 NTU. Experimental results indicate that red light achieves the optimal polarization imaging performance, followed by green light, while blue light performs the weakest. Furthermore, a polarization image enhancement algorithm is proposed, which significantly improves the imaging quality for all three laser wavelengths. Under a turbidity condition of 19.97 NTU, the entropy value of enhanced images of diving suit fabric using the proposed method shows an approximately 34.4% improvement compared to the traditional Schechner method. The research demonstrates that integrating polarization imaging into active laser imaging systems can effectively enhance underwater imaging quality, offering new insights for optimizing underwater imaging technology at specific wavelengths.
-
zhangsiyao,wuchenyang,Horst Vogel,yuanshuguang
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20250317001
Abstract:
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) constitute a crucial superfamily of membrane proteins that play a pivotal role in cellular signal transduction and serve as primary targets in contemporary drug development. The β2-adrenergic receptor (β2AR), a representative member of class A GPCRs, is a critical target in the therapeutic management of respiratory diseases. Despite the availability of several β2AR agonists in clinical practice, there remains a substantial need for optimization concerning drug safety, efficacy, and receptor selectivity. In this study, a virtual screening approach was utilized to effectively identify β2AR agonists from a compound library comprising 19 million molecules. Through comprehensive cellular assays and in vivo pharmacokinetic evaluations, a novel short-acting agonist with an EC50 value of 0.86 nM was discovered, presenting a promising candidate for the development of next-generation treatments for respiratory diseases.
-
zhoumengbing,liqiuyan,wuou,wangyang
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241203002
Abstract:
Currently, AI application workloads, represented by machine learning, exhibit a dual-density characteristic, combining both compute-intensive and data-intensive traits. These applications not only require support for the storage, transmission, and fault tolerance of massive data but also need to optimize the performance of complex logical computations. Traditional single big data frameworks or high-performance computing frameworks can no longer meet the challenges posed by these applications. The hybrid big data platform based on Spark and MPI proposed in this paper is a high-performance big data processing platform. This platform, built on a typical large-scale cluster, focuses on addressing the storage and computing characteristics of dual-density applications, such as those in machine learning, and includes three key modules: dual-paradigm hybrid computation, heterogeneous storage, and integrated high-performance communication. To address the dual-density nature of these applications, which involve both data-intensive big data processing and compute-intensive high-performance computing, a computational module combining the Spark and MPI paradigms is designed. By splitting and classifying tasks, compute-intensive tasks are offloaded to the MPI computation module, enhancing the dual-paradigm hybrid computation capability. To address the different data characteristics during the computation process, a heterogeneous storage structure and a data-metadata separation strategy are designed. This optimizes data storage through classification, building a highly available, high-performance storage system. In response to the communication needs of dual-density computing, a high-performance communication technique is proposed, providing strong communication support for the computing and storage modules. Test results show that this platform provides efficient dual-paradigm hybrid computation for dual-density applications, achieving performance improvements of 4.2% to 17.3% compared to a standalone Spark big data platform for various computation tasks.
-
YU Xuan,YANG Changjiang,CUI Xu,CHEN Liang
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20250323001
Abstract:
Targeted protein degradation technologies face significant challenges, including insufficient target specificity and low delivery efficiency. Mesoporous bioactive glass (MBG) is a biocompatible nanomaterial widely studied in drug delivery, yet its potential as a platform for targeted protein degradation remains unexplored. In this study, FITC labeling and the biotin-avidin system were employed to evaluate the subcellular localization of MBG and its potential as a protein degradation carrier. Additionally, the ferroptosis-inducing capability of Fe-doped MBG was investigated. The results demonstrated that MBG facilitates the internalization of target proteins and degradation in lysosomes, as exemplified by the degradation of PD-L1. Furthermore, MBG was shown to deliver iron ions into lysosomes, inducing ferroptosis. This study, for the first time, reveals the dual functionality of MBG in targeted protein degradation and ferroptosis induction, offering an innovative approach for the spatiotemporally controlled synergistic treatment of cancer through "protein degradation-ferroptosis" strategies.
-
Xing Ze Ming,Gong Jia Yuan,Chen Hong Yang,Chen An Qing
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241207001
Abstract:
In order to better monitor the health state of power lithium batteries. A lithium battery health state prediction method based on Improved Bidirectional Temporal Convolutional Network, Long Short Term Memory Network and Attention Mechanism is proposed. The hyperparameters of the proposed method are optimized using Crested Porcupine Optimizer. Tests were conducted on the University of Maryland lithium battery charge/discharge dataset to extract capacity-related health features, and the health features with higher correlation were screened by Pearson correlation coefficient as inputs to the neural network algorithm. The Root Mean Squard Error of the proposed method is no more than 0.020, the Mean Absolute Error is no more than 0.017, and the R-Square is above 0.995 for all battery health state predictions. Higher accuracy can be achieved in lithium battery health state prediction.
-
Xu zhouyi,Zhang fan,Zhang lei,Yu jie,Cao xiuhua,Fu zhenxiao,Sun rong
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241201004
Abstract:
As the internal electrode materials in multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) are increasingly being replaced by base metals such as nickel instead of precious metals, the sintering process must be conducted in a reducing atmosphere. This work investigates the properties of Mn-doped BaTiO3-based ceramics sintered under different reducing atmospheres, exploring the effect of varying H?/N? ratios on dielectric performance and reliability. BaTiO3-based ceramics were prepared using the solid-phase method under different reducing atmospheres. X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Raman spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were employed to characterize the microstructure and properties of the samples. The study found that the polarization mechanism significantly affects the dielectric performance and reliability of BaTiO3-based ceramics. Specifically, as the reducing atmosphere intensifies, the polarization mechanism transitions from short-range defect dipole polarization to long-range defect carrier polarization, impacting the dielectric constant, dielectric loss, and insulation resistance. The sample sintered under 1.5% H?/98.5% N? (S2) exhibited the highest dielectric constant, lowest dielectric loss, and best insulation resistance, demonstrating excellent overall performance. Additionally, BaTiO3-based MLCCs with thickness of 0.9 μm and the TCC of X7R were successfully fabricated. This work provides theoretical and technical guidance for improving the dielectric performance and reliability of BME-MLCCs.
-
Zhu Donglin,Chen Miao,Mao Yuyan,Zhang Junhao,Wang Zhongli
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241127002
Abstract:
3D scene reconstruction is a critical research topic in autonomous driving, robotics, and related fields, with extensive applications in navigation mapping, environmental interaction, and virtual/augmented reality tasks. Current deep learning-based reconstruction methods can be primarily categorized into five groups from the perspectives of scene representation and core modeling techniques: cost volume-based depth estimation methods, truncated signed distance function (TSDF)-based voxel approaches, transformer architecture-based large-scale feedforward methods, multilayer perceptron (MLP)-based neural radiance fields (NeRF), and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Each category exhibits unique strengths and limitations. The emerging 3DGS method distinguishes itself by explicitly representing scenes through Gaussian functions while achieving rapid scene rendering and novel view synthesis via efficient rasterization operations. Its most significant advantage lies in diverging from NeRF''s MLP-based scene representation paradigm - 3DGS ensures both efficient rendering and interpretable editable scene modeling, thereby paving the way for accurate 3D scene reconstruction. However, 3DGS still faces numerous challenges in practical scene reconstruction applications. Based on this analysis, this paper first provides a concise introduction to 3DGS fundamentals and conducts comparative analysis with the aforementioned four categories. Following a systematic survey of existing 3DGS reconstruction algorithms, we summarize the key challenges addressed by these methods and review current research progress on core technical difficulties through representative case studies. Finally, we prospect potential future research directions worthy of exploration.
-
Huai wentao,Li Zhichao,Zhang lei,Yv jie,Cao xiuhua,Fu zhenxiao,Sun rong
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241201001
Abstract:
The study investigates the influence of different raw material particle sizes of barium titanate (BaTiO?, BT) on the dielectric properties of ceramics and aims to optimize their electrical performance through doping modifications. Ceramic samples were prepared using BT powders with particle sizes of 100 nm, 150 nm, 200 nm, and 250 nm via the solid-state ball milling method. Y?O?, Ho?O?, MgO, and SiO? were introduced as dopants to control grain growth and tailor the dielectric properties. The microstructure and dielectric characteristics of the ceramic samples were systematically analyzed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and dielectric measurements. The results revealed that the BT-10 sample exhibited significant dopant diffusion, which hindered the formation of an ideal "core-shell" structure and reduced tetragonality. While BT-10 showed a relatively high dielectric constant, its temperature stability was poor. In contrast, the BT-15, BT-20, and BT-25 samples successfully formed a "core-shell" structure, with BT-25 demonstrating the highest tetragonality. The BT-25 sample exhibited the most favorable electrical performance, including the highest saturation polarization strength (Ps = 11.817 μC/cm2), remanent polarization strength (Pr = 1.465 μC/cm2), and superior dielectric stability under DC bias conditions. These findings indicate that the BT-25 sample offers the most balanced and optimized overall performance. Furthermore, the study highlights the challenges associated with using smaller BT particle sizes in fabricating "core-shell" structured ceramics, particularly the increased specific surface area and higher defect density of BT powders. This research provides valuable theoretical insights and technical guidance for optimizing the dielectric layers of multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs).
-
Dou Ming Yang,Geng Yan Juan,Yang Jiabin
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241030001
Abstract:
Hand pose estimation based on RGB images shows crucial application prospects in the fields of dynamic gesture recognition and human-computer interaction. However, existing methods face numerous challenges. For example, the high degree of self-similarity of the hand and the extremely dense distribution of key points make it extremely difficult to achieve high-precision prediction under the condition of low computational cost, which in turn leads to limitations in performance in complex scenarios.In view of this, this paper proposes a two-dimensional (2D) hand pose estimation model based on the YOLOv8 network, namely FAR-HandNet. This model ingeniously integrates the Focused Linear Attention module, the key point alignment strategy, and the regression residual fitting module, effectively enhancing the feature capture ability for small target areas (such as the hand), while reducing the adverse impact of self-similarity on the positioning accuracy of hand key points. It is worth mentioning that the regression residual fitting module uses a flow-based generative model to fit the distribution of key point residuals, which greatly improves the accuracy of the regression model.The experiments in this paper are carried out on the CMU and FreiHAND datasets. The experimental results clearly show that FAR-HandNet has obvious advantages in terms of the number of parameters and computational efficiency, and performs excellently in PCK (Percentage of Correct Keypoints) under different thresholds, showing a significant improvement compared with existing methods. In addition, the inference time of this model is only 32ms. The ablation experiments further confirm the effectiveness of each module, fully verifying the effectiveness and superiority of FAR-HandNet in the hand pose estimation task.
-
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241122001
Abstract:
The loss of upper limb function brings a lot of inconvenience to the life of amputees. In order to improve the life quality of upper limb amputees, it is necessary to develop a low-cost, lightweight and powerful prosthetic system. In this paper, a three-degree-of-freedom modular light-weight upper limb prosthetic arm and its multi-joint cooperative control system are designed to provide a lightweight, economical, modular and comprehensive prosthetic solution. By using the hollow structure design, the overall weight of the prosthetic arm is significantly reduced (about 2 kg), which is much lower than existing commercial prosthetic products, while ensuring the number of degrees of freedom and effectively reducing manufacturing costs, improving the comfort and suitability of the prosthetic arm. In addition, the multi-joint control system designed in this paper, combined with the precise coordination algorithm, can accurately control each joint to reach a predetermined Angle at the same time, to meet the needs of different degrees of amputees for multi-joint cooperative movement. Through precision and efficiency tests, the results show that the prosthesis performs well in terms of control accuracy, and the motion efficiency can meet most of the needs of daily life.
-
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241129002
Abstract:
Currently, with the exponential growth of data on the internet, the complexity of big data processing systems has also increased dramatically. To adapt to changes in factors such as cluster resources, datasets, and applications, big data processing systems provide adjustable configuration parameters tailored to different application scenarios. Among these systems, Spark is one of the most popular and contains over 200 configuration parameters for controlling parallelism, I/O behavior, memory settings, and compression. Incorrect configuration of these parameters often leads to severe performance degradation and stability issues. However, both ordinary users and expert administrators face significant challenges in understanding and tuning these settings for optimal performance, resulting in substantial human and time costs. In the tuning process, selecting unreasonable parameter ranges can increase time costs by fivefold, or even worse, cause operational failures in the cluster and terminate system operation—an incalculable loss for large-scale clusters serving customers.
-
JIANG Biao,ZHENG Jianglong,Huang Xiaoxin,Li Zhifeng,Li Linwei,HUANG Yifan
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241010001
Abstract:
Electromagnetic pulse sound source (Boomer) is a commonly used explosion sound source in marine seismic exploration, and the deep-sea application of such explosion sound source needs to solve cavitation suppression problem. In this paper, a deep-sea boomer source based on pressure compensation balance is proposed. A boomer transducer with a maximum working pressure of 20MPa is developed and tested in a high-pressure anechoic tank. Through the analysis of the hydrophone outputs under different energy and pressure levels, it can be seen that an air sac with the initial pressure of 0.5MPa can effectively balance the internal and external pressure of the transducer, solve the problem of cavitation suppression, and realize the excitation of broadband pulse sound waves. The repeatability of the acoustic wave is very good, and the minimum correlation coefficient is to 0.986. With the increase of working pressure from 0.5MPa to 20MPa, the main change in acoustic characteristics is the amplitude attenuation (204.6dB to 194.2 dB) and width compression (182μs to 88μs), and the main frequency (2.3kHz as the center) slightly shifted to high frequency. Compared with the hydrophone output in the process of pressure rising and downing in the high-pressure anechoic tank, it can be seen that the repeatability of the acoustic wave is better. The higher the pressure, the better the waveform consistency, indicating that the boomer transducer based on pressure compensation balance has a more stable performance under high pressure environment.
-
Daiwei,Zhanghaoxuan,Chenfangxu,Pengwei
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241012001
Abstract:
Cancer is a genetically related disease with multiple subtypes, each exhibiting significant differences in genetics, phenotype, and treatment response. Accurate classification of cancer subtypes is critical for personalized treatment, as it helps improve therapeutic outcomes. However, cancer subtype classification methods based on patient gene expression data often struggle to effectively distinguish rare subtypes in the presence of imbalanced samples. To address this issue, a cancer subtype classification method called MFP-VAE (Meta-learning Few-shot Prototype learning VAE) is proposed, focusing on handling datasets with imbalanced samples. This method improves the sampling strategy to ensure balanced consideration of different subtypes in meta-learning tasks. The model employs a variational autoencoder for feature extraction and classifies samples by calculating the distance between the samples and the subtype prototypes. Experimental results show that MFP-VAE outperforms existing methods on two public cancer datasets, significantly improving classification accuracy, especially under imbalanced sample conditions. Furthermore, survival analysis reveals that the distinguished cancer subtypes exhibit significant differences in clinical characteristics, providing meaningful clinical insights.
-
Li Yisheng,Xu Yongjie,Wang Shuqiang,Wang Yishan
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241127001
Abstract:
With the rapid development of deep learning technology, autism screening based on neural signals such as Electroencephalography (EEG) is gradually emerging as a novel diagnostic approach. However, due to the complexity of EEG data acquisition, especially for children, insufficient data often poses a challenge. Data augmentation methods are commonly used to address the scarcity of real-world data, with Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) being a frequently applied technique. However, due to the limited scale and diversity of data, current augmentation methods have yet to achieve optimal classification performance. This study introduces an improved conditional diffusion model to enhance both raw EEG signals and their corresponding functional connectivity temporal graphs. Experimental results demonstrate that this method significantly improves autism classification performance, achieving maximum classification accuracies of 84.38% and 79.01% for resting-state and task-state data, respectively. These findings validate the effectiveness of data augmentation based on the conditional diffusion model in enhancing autism screening outcomes.
-
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241201003
Abstract:
Existing indoor three-dimensional (3D) object detection is able to detect a limited number of object categories, thus limiting the application on intelligent robotics. Open vocabulary object detection is able to detect all objects of interest in a given scene without defining object categories, thus solving the shortcomings of indoor 3D object detection. At the same time, the large language model with prior knowledge can significantly improve the performance of visual tasks. However, existing researches on open-vocabulary indoor 3D object detection only focuses on object information and ignores contextual information. The input data for indoor 3D object detection is mainly point cloud, which suffers from sparsity and noise problems. Relying only on the object point cloud can negatively affect the 3D detection results. Contextual information contains scene information, which can complement the object information to promote the recognition on object category. For this reason, this paper proposes an open vocabulary 3D object detection algorithm based on contextual information assistance. The algorithm integrates contextual information and object information through a large language model, and then performs chain-of-thought reasoning. The proposed algorithm is validated on SUN RGB-D and ScanNetV2 datasets, and the experimental results show the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
-
ZHENG Jianglong,JIANG Biao,Li Zhifeng,Huang Xiaoxin,Li Linwei,HUANG Yifan
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241205001
Abstract:
The high-pressure anechoic tank is an important experimental testing platform for the development of deep-sea transducers, sensors, and other acoustic instruments and equipment. In this paper, background noise and acoustic field fluctuations at different frequencies were measured for the homemade 20MPa high-pressure anechoic tank. The echo interference level under fixed measurement position and distance conditions was calculated, and the echo interference curve was drawn. The time-frequency characteristics of signals under typical low-frequency and high-frequency conditions were analysed. The measurement results of background noise show that although the background noise inside the tank is relatively high and has characteristic peaks in the frequency range of 10-12kHz, it allows for measurement experiments with sufficient signal-to-noise ratio conditions. Meanwhile, the time-domain waveform results of sound field fluctuations measured in different frequencies show that the signal amplitude rapidly decays after a transmission width of 2ms, and the higher the frequency, the faster the attenuation, indicating that the sound absorption cone inside the tank has a good sound absorption effect. The calculation results of echo interference level show that most frequency points above 10kHz do not exceed ± 1dB. The designed fixed measurement position meets the requirements of free field testing, especially the echo interference of frequency points such as 20kHz, 28kHz, and 34kHz does not exceed ±0.5dB, which meets the requirements of precision measurement.
-
Liu Gaocheng,Tong Jiabo,Yang Shilin,Wang Qiuying,Tang Xinyu,Liu Chang,Liu Jia
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20250118001
Abstract:
The reconstruction of cerebral blood flow velocity (CBFV) is essential for the long-term assessment of cerebrovascular function. To this end, this study proposes a multivariate time-series model based on a Transformer encoder to reconstruct CBFV signals. The model utilizes time-series signals of arterial blood pressure (ABP) and CO2 to achieve accurate CBFV reconstruction. A long short-term memory (LSTM) module is introduced into the model to address the limitation of dispersed global attention in the attention mechanism, thereby enhancing the processing of local details. Additionally, a mixed loss function is employed to control local waveform errors, improving reconstruction accuracy. Furthermore, a transfer learning strategy is designed based on the correlation between ABP and electrocardiogram (ECG) signals to alleviate the impact of data scarcity on the reconstruction task. Experimental results on the cerebrovascular regulation dataset of diabetic patients from Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms existing regression models and deep learning models in CBFV reconstruction tasks. The results show a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.518, a dynamic time warping distance of 17.879, and a mutual information value of 0.343 between the reconstructed and true values. Additionally, the model can reconstruct 200 data points within 0.04 seconds.
-
liujinqing,sunrenyun,zhaoling,zhangguohao,hezihao
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241204002
Abstract:
Based on the path planning method that ensures tangency between arcs and straight lines, potential collision conditions during parking are analyzed. Moreover, parking path planning for oblique spaces is conducted, with obstacles and parking space boundaries evaluated in detail to ensure the reasonableness of the planning. Additionally, a collision constraint model for the parking path is constructed to account for the dynamic characteristics and geometric constraints of vehicle motion. Distance equations for critical collision conditions are developed to determine safe distances and effective areas during parking maneuvers. Simulation experiments conducted under various working conditions demonstrate that collision avoidance is effectively achieved through the path planning method, which aligns with the vehicle"s traveling direction and accommodates varying lane widths. Ultimately, the validity of the planned paths is verified, and the safety and adaptability of these paths are assessed to ensure secure parki
-
zhangjiashuai,yangliuqing,fuqilin,chenghuiwu,shaocuiping,lihuiyun
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20240914001
Abstract:
Chiplet-based multi-chip integration designs provide a flexible and scalable solution that surpasses traditional SoC (System on Chip) monolithic integration. However, inter-chiplet communication has become a significant bottleneck affecting overall system performance. The Network on Interposer (NoI) plays a pivotal role in multi-chip systems, directly influencing both performance and development costs. In this paper, we review NoI communication topologies for heterogeneous chiplets. We thoroughly explore the importance of current inter-chiplet communication architectures and discuss their design and implementation methods. This paper covers the entire communication process, spanning from protocol and interface layers to the application layer, classifying interconnect topologies based on their structural configurations and providing in-depth analyses and cross-comparisons for each category. Furthermore, we investigate future directions in NoI communication technologies, identifying technical challenges and potential solutions. We also propose advanced evaluation methods and modeling techniques for reusable interposer layers and topologies. This review aims to provide researchers with a thorough understanding of the current landscape and future trends in NoI technology, emphasizing its crucial role in advancing next-generation semiconductor devices across a wide spectrum of applications.
-
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20240612001
Abstract:
In the era of big data, the storage of massive amounts of data has become a challenging problem. DNA storage technology, as a cutting-edge solution to this challenge, particularly focuses on the development and challenges of information editing technology. Initially, DNA storage primarily served "cold" data, but the latest advancements in the technology have driven its development towards supporting data updates and management for more advanced applications. This paper proposes an incremental management method for secure DNA storage, designing a hybrid encryption mechanism that supports multi-party editing and a DNA incremental storage model. While ensuring security, this model achieves secure and efficient information editing and management under existing technological constraints through a partitioned storage scheme and efficient indexing encoding. This approach meets the modern data management requirements for flexibility and cost-effectiveness, providing new perspectives and strategies for addressing core issues in DNA data management.
-
wei wu,gong jia yuan,che kai,zhu zheng ze
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20241207002
Abstract:
To enable autonomous driving systems to effectively detect and locate road potholes in complex environments, improvements have been made to the existing YOLOv5 object detection algorithm. Firstly, MobileNetV3 is employed to replace the original backbone of the model, reducing the parameter count and achieving a more lightweight network design. Additionally, a BiFPN (Bidirectional Feature Pyramid Network) module is introduced in the neck of YOLOv5, significantly enhancing the model"s performance in multi-scale feature fusion, information propagation, feature representation, and detection accuracy, while maintaining the lightweight nature of the architecture. Furthermore, the concept of image style transfer from Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) is incorporated, utilizing PaddleGAN for data augmentation to increase the diversity of the dataset. Finally, experiments conducted on a custom dataset revealed that the improved YOLOv5 algorithm achieved a 3.5% increase in accuracy, a 0.9% improvement in mAP, and an enhancement in detection speed by 5.8 frames per second (fps). The proposed algorithm is more lightweight and enhances detection precision, providing a valuable technical reference for pothole detection in complex environments.
-
kangjianjun,niejunxi,jingjialu,changyiting,zhouwenqing,liuchaoran
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20240828001
Abstract:
This article introduces a modular design concept that can realize the general observation of marine environment and multi -equipment integration of the universal marine buoyant data collection system. This system uses ARM chip timer and interrupt controller to virtually collects multi -module parallel collection processing circuits. The full system is divided into three modules: meteorological security, hydrotoma and communication according to the function of marine data buoyoma functions, and realizes the continuous collection and processing of buoyant multi -equipment, as well as real -time two -way communication. The serial extension chip realizes the system interface expansion, which improves the system"s installation capacity from the hardware. The communication module uses DMA technology to realize the functions of real -time data of dual -road real -time data, which realizes the reliable and safe operation of the buoyant system on the sea, and also improves its human -computer interaction function. This system has verified the stability, reliability, and measurement accuracy of the system through laboratory testing and operation experiments at sea.
-
Liang Zhanxiong,Sun Xudong,Cai Yonda,Zhang Yuming,Mai Langjie,He Yulin,Huang Zhexue
DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.20240224001
Abstract:
LOGO is a new distributed computing framework using a Non-MapReduce computing paradigm. Under the LOGO framework, big data distributed computing is completed in two steps. The LO operation runs a serial algorithm in a number of nodes or virtual machines to process independently the random sample data blocks, generating local results. The GO operation uploads all local results to the master node and integrate them to obtain the approximate result of the big data set. The LOGO computing framework eliminates data communication between nodes during iterations of the algorithm, greatly improving computing efficiency, reducing memory requirements, and enhancing data scalability. This article proposes a new distributed machine learning algorithm library RSP-LOGOML under the LOGO computing framework. A new distributed computing is divided into two parts: the serial algorithm executed by the LO operation and the ensemble algorithm executed in the GO operation. The LO operation can directly execute existing serial machine learning algorithms without the need to rewrite them according to MapReduce. The GO operation executes ensemble algorithms of different kinds depending on the ensemble tasks. In this article, the principle of LOGO distributed computing is introduced first, followed by the algorithm library structure, the method for packaging existing serial algorithms and the ensemble strategy. Finally, implementation in Spark, App development, and the results of performance tests for various algorithms are demonstrated.
The "In Press" section displays the articles officially accepted after peer review. These articles are currently under copyediting process without volume/issue information, but are citable according to their Digital Object Identifiers(DOI).
-
Special Issue of the 1st CCF Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, CIVS 2023
人工智能与新能源汽车的交叉融合为现代汽车工业和交通体系带来了深刻的变革,这种协同进化的发展趋势不仅推动了智能汽车产业的快速崛起,也在技术层面提出了全新的挑战。如何解决智能系统面向复杂场景的计算能力、实时性、可靠性、能耗、成本等关键问题,是未来智能汽车领域研究和产业应用的重要方向。
View
本期专刊聚焦探讨我国智能汽车领域的最新研究成果,主要介绍相关学者在智能感知、决策规划、执行控制等关键领域的研究进展以及对未来发展趋势的展望与分析。 -
Government Big Data Management and Intelligent Services
在“互联网+”环境下,政务大数据关联公共服务数据和社会传感数据,综合共享、分析和利用这些资源,将使城市管理模式从单一走向立体,使城市服务系统从孤立走向共享,使城市决策模式从机械走向智能。因此,迫切需要建立有关政务大数据管理、业务协同和智能服务的新理论、新技术和新平台,以提升城市管理和政府应急指挥决策能力。为促进互联网+政务大数据管理与智能服务,本刊特请国际欧亚科学院院士、中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院院长樊建平研究员、澳门大学科技学院院长须成忠教授、中山大学沈鸿教授、中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院尹凌研究员担任客座编辑,共同组织“政务大数据管理与智能服务专题”,以期为读者呈现该领域的研究进展与发展趋势。
View -

Mechanisms and Robotics—Innovative Tools for Modern Machines and Equipments (I)
建立现代机器与装备的原始创新能力是现代产业获取自有知识产权、提升国际市场竞争力的核心手段,是我国实现由制造大国向制造强国顺利转变的必然要求。对于以机械运动作为功能实现手段的现代机器与装备来说,其原创研发的核心问题是其功能机理的探究及其机械运动过程的构思、规划与实现问题,这正是现代机构学与机器人学的核心研究议题。为推进理论与应用深度互动,促进现代机器与装备原始创新与研发相关理论、方法、技术和应用的进步,特邀请上海交通大学郭为忠教授、中科院深圳先进院何凯老师担任客座编辑组织“机构与机器人学——现代机器与装备的创新利器”专题,分两期刊出,以期读者了解和关注该领域的研究进展与发展趋势。
View -

-

3D Vision and Visualization
In recent years, the concept of "Metaverse" has become popular again, and Facebook has even changed its name to "Meta" to embrace the metaverse. Metaverse is a concept created by the famous American science fiction writer Neal Stephenson in the novel "Snow Crash" published in 1992. Its core is to build a virtual digital world parallel to the real physical world.
But how to construct a virtual mirror of the real physical world is a key technical issue in realizing the metaverse. Vision is one of the most important ways for humans to perceive the world. With the continuous progress of 3D sensing technology, the rapid development of deep learning and the explosive growth of 3D visual data, the acquisition, analysis, understanding, expression, modeling, presentation, interaction and visualization of 3D visual data have become the core research issues in the construction of virtual images to the real world.
Our journal is honored to invite Professor Chen Baoquan, Executive Director of the Frontier Computing Research Center of Peking University, and Researcher Cheng Zhanglin of Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Science to serve as guest editors of the special issue to share the research advancements of Chinese scholars on 3D vision and visualization.
View -

 Special Issue
Special Issue-
XIONG Gang,MENG Jiao,CAO Zi-gang,WANG Yong,GUO Li,FANG Bin-xing
2012,1(1):32-42 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201205006
Abstract:
Nowadays, with the rapid development of the Internet, more and more new applications appear gradually, the scale of network expand constantly, and the architecture of network is more and more complicated. As one of the basic technologies for enhancing network controllability, traffic classification can not only provide better QoS for ISPs, but also supervise and manage network effectively, which can ensure the security of the Internet. In this paper we review the research methods and achievements in the field of traffic classification, compare these traditional methods, and point out their advantages and disadvantages. On the other hand, for the real challenges of real-time classification of high-speed network environment, encrypted traffic classification, fine-grained traffic classification, and dynamically changed protocols classification, we describe and analyze the related research progress. Finally, we look ahead the future research direction.
-
GE Ruiquan, WANG Pu, LI Ye,CAI Yunpeng
2017,6(5):55-68 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201705006
Abstract:
Repetitive sequences are prevalent in genomes. A large number of experiments have confirmed that they play an important role in biological evolution. At present, the discovery and detection of the repetitive sequences have been becoming a hot topic of genomics. This paper summarizes the research progress in this regard, and briefly analyses the associated tools. Finally, the development of repetitive sequences in future is prospected.
-
2012,1(3):1-9 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201209001
Abstract:
The technology of the robot represents a national high-tech level and the degree of automation. It is helpful to develop the industry of service robots in China if we know the current situation and development trend of service robots research clearly. Recently, robotic cleaners and educational robots have been in great demand. Entertainment robots and surveillance robots are developed rapidly and the market expands quickly. Medical robots begin to enter the modern life and have played an important role in the modern surgery. To satisfy the great market and shorten the distance between China and developed countries, it is necessary to capture the development trend of the technology of service robots. R&D on service robots should focus on the integrated technologies on intelligence, modularization and network.
-
YAN Xiaoqing,CHEN Hongyun,WU Binbin,LIU Chunhua,LIANG Yan
2015,4(4):87-93 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201504010
Abstract:
The human gut is densely populated by the gut microbiota. There are accumulating evidences indicating that the gut microbiota plays a significant role in the function of the body, which including the metabolism and energy absorption, the development in the function of gastrointestinal, the modulation of immune system and so on. Many chronic diseases, such as obesity, obesity-associated inflammation, inflammatory bowel disease and depression, are related to gut microbiota dysbiosis. The research of the interaction between intestinal bacteria and human body is instructive to the prevention or treatment of many chronic diseases and maintaining health.
-
ZHOU Wu,XIE Yaoqin,TIAN Yangyang
2014,3(1):68-76 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201401007
Abstract:
The accurate contour delineation of the target and organs at risk (OAR) is essential in treatment planning for image guided radiation therapy. In clinical applications, the contour delineation is often done manually by clinicians, which may be accurate, but time-consuming and tedious for users. Although a lot of automatic contour delineation approaches have been proposed, few of them can fulfill the necessities of applications in terms of accuracy and efficiency. In this work, a novel approach of target delineation was proposed. Target delineation of OARs was achieved by using snake model and multiscale curve editing to obtain promising results. It allows users to quickly improve contours by a simple mouse click. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method for clinical target delineations.
-
2012,1(3):20-24 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201209004
Abstract:
Gene is the genetic material basis. All life phenomena, like disease and death, are related to Gene. Gene sequencing is a way to read life. With the development of new generation high-throughput sequencing technology, TB or more sequence data will be generated daily. It’s more difficult to interpret these big and complex data than to acquire them. Sequence data interpretation is a critical step in current biological research and has great practical significance. It’s a great challenge for current computer systems and computing models to store, process and analysis massive high throughput sequence data. With survey, especially from BGI (Beijing Genome Institute), the current status, problems and measures taken to process high throughput sequence data will be discussed. However, the challenge is too big to be solved unless more people in different fields work together in depth for a long term.
-
2012,1(1):48-54 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201205008
Abstract:
This paper gives a comprehensive introduction to the status of current machine translation research and technology, and analyzes the key problems to be resolved. Finally our idea of the future trends and prospects of machine translation are put forward.
-
ZHANG Yihong,XU Wenjing,YANG Kun
2014,3(5):19-27 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201405003
Abstract:
As an advanced biosensing strategy, the electrochemical biosensor is made up of the active sensing biomaterial and the electrochemical signal transducer, and is being widely applied in the fields of clinical medicine, drug and food analysis as well as the environmental monitoring. The electrochemical biosensor has the advantages of excellent specificity, high sensitivity and simplicity. This review focused on the fundamental principle of electrochemical biosensor, its classification and the biomedical applications. The prospect of the electrochemical biosensors was outlined as well.
-
2012,1(1):6-14 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201205002
Abstract:
With the increasing concerns of global warming and resource constraints, electric vehicles (EVs) have made great progress during the past decade. The electric driving system of EVs has dinstinct advantages, such as quick response, easy measurement , and precise control of motor torque, available flexible driving architecture, and regenerative braking, etc. Such advantages can be used to improve the performance of vehicle dynamic control. This paper presents the recent research efforts on electric vehicle dynamic control in terms of parameters estimation and dyanmic control scheme and methodology, especially focusing on the tire-road friction estimaion , novel traction control methods. The lateral dynamic control including the electrical differential control, direct yaw moment control, and the integratin chassis cotrol is proposed. Several prospects for vehicle dynamic control are proposed.
-
2013,2(4):49-55 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201307009
Abstract:
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive technique that can be used for brain studying and clinical therapy. Firstly, the technology feature and application of the TMS instrument were introduced. Then several TMS coil positioning methods were evaluated and several key problems about TMS coil positioning were discussed. The aim of this study was to propose a new method for TMS coil positioning. The new method combines three aspects of quantitative information including the brain scalp, brain anatomy and brain function and has great advantages and broad application prospects.
-
2017,6(3):29-40 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201703003
Abstract:
Automatic drive is an important application field of artificial intelligence. In this paper, a novel training strategy for self-driving vehicles was investigated based on the deep reinforcement learning model. The proposed method involves a Q-learning algorithm with filtered experience replay and pre-training with experiences from professional drivers, which accelerates the training process due to reduced exploration spaces. By resampling the input state after clustering, generalization ability of the strategy can be improved due to the individual and independent distribution of the samples. Experimental results show that, in comparison with conventional neural fitted Q-iteration algorithm, the training efficiency and controlling stability can be improved more than 90% and 30% respectively by the proposed approach. Experimental results with more complex testing tracks show that, average travel distance can be improved more than 70% in comparison with the Q-learning algorithm by the proposed method.
-
2012,1(3):66-71 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201209012
Abstract:
Hadoop job schedulers typically use a single resource abstraction and resources are allocated at the level of fixed-size partition of the nodes, called slots. These job schedulers ignore the different demands of jobs and fair allocation of multiple types of resources, leading to poor performance in throughput and average job completion time. This paper studies and implements a Muti-resource Fair Scheduler (MFS) in Hadoop. MFS adopts the idea of Dominant Resource Fairness (DRF). It uses a demand vector to describe demands for resources of a job and allocates resources to the job according to the demand vector. MFS uses resources more efficiently and satisfies multiple jobs with heterogeneous demands for resources. Experiment results show that MFS has higher throughput and shorter average job completion time compared to Hadoop slot-based Fair Scheduler and Capacity Scheduler.
-
HU Chao,SONG Shuang,YANG Wan-an,MENG Qing-hu,LI Bao-pu,ZENG De-wen,LI Xiao-xiao,ZHU Hong-mei
2012,1(1):105-113 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201205017
Abstract:
Wireless Capsule Endoscope (WCE) is a very promising tool for the examination of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. However, there are some problems to be solved for the existed WCE, and one key problem is the accurate localization and tracking of the WCE. Among the possible localization methods, the magnet-based localization technique has its advantages: no need for power, not much space occupation, continuously tracking ability, and no negative effect. In this paper, we present the localization method for the magnet objective inside the WCE based on the magnetic sensor array outside the human body. Through the algorithm and system design we realize real time tracking of 3D position and 2D orientation of the magnet based on the magnetic dipole model. In order to overcome the interference of the human body movement, we propose the multi-magnets’ localization method; also, the 3D positioning and 3D orientation method is proposed, which can be used to make the 3D recovery of the GI tract and the accurate computation of the physiological tissue parameters. The real experiments show that the proposed localization system can run well and obtain the accuracy with 2~3mm for the magnet.
-
SHEN Yang,LING Tao,YAO Hui,LI Yan-ming,JIN Qiao-feng,ZHENG Hai-rong
2012,1(1):93-99 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201205015
Abstract:
For the advantages of noninvasive, real-time and quantitative detection, ultrasonic transient elastography has important clinical application value. This work investigates the transient elastography in a few ways and aims to design a transient imaging system. The Displacement tracking algorithm based on correlation techniques and the parabolic interpolation algorithm is proposed to improve the accuracy. A novel match filter is designed to convolute with the estimated displacement in the time direction to boost the SNR of the displacement for a better strain image mapping. The convoluted result shows the match filter can significantly improve the strain image quality and help getting more accurate Youngs modulus estimation. The Time Gain Compensation (TGC) circuit is designed to compensate the attenuated power of the ultrasound signal. And a modified polyacrylamide gel based tissue-mimicking phantom is also developed in this paper, both indentation testing and transient elastography are used to characterize the elastic properties of this phantom. The results are almost consistent with each other.
-
CHI Xue-bin,XIAO Hai-li,WANG Xiao-ning,CAO Rong-qiang,LU Sha-sha,ZHANG Hong-hai
2012,1(1):68-76 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201205011
Abstract:
This paper introduces the scientific computing grid, ScGrid, and it’s middleware SCE. ScGrid is built as one virtual supercomputer, integrating computing resource from more than 30 institutes. It provides unified,?easy to use and reliable scientific computing services. SCE is a lightweight grid middleware, which supports global job scheduling and unified data view. It provides multiple user interfaces including command line, grid portal and APIs. At present, ScGrid has been very successfully used in Chinese Academy of Sciences and widely accepted by more than 200 users.
-
ZHANG Hao-shi,WU Zhen-xing,TIAN Lan,YANG Lin,LI Guang-lin
2012,1(1):114-118 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201205018
Abstract:
Effectively reducing power line interference is always an important issue in electromyography (EMG) signal recordings and analysis. In this study, four commonly used de-noising methods, including digital notch, LMS based adaptive filter, Kalman filter and S transform, which may be suitable for the reduction of power line interference in real-time EMG recordings, were chosen and their performance in reducing the power line interference from EMG signal recordings were quantitatively analyzed and compared. The pilot results of this study showed that Kalman filter presented the best whole performance in attenuating power line interference from EMG signals and S transform de-noising method illustrated the best performance when the power line interference was severe.
-
2012,1(3):47-54 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201209009
Abstract:
With the rapid increase in numbers and scales of deep web sites on the Internet, search for data or information from deep web sites by submiting queries to and obtaining results from the backend databases has become a major means in information retrieval from the Web. This area has attracted many researchers to devote their efforts on development of technologies to make better use of information in th deep web. One challenge is searching for and integration of data from various databases in deep web. Since deep web is dominated by text data, research and development of technologies for text information retrieval from deep web have a broad application potential. In this paper, we review the state-of-the-art of deep web research in details and propose some future research directions.
-
LUO Li,YANG Chao,ZHAO Yu-bo,CAI Xiao-chuan
2012,1(1):84-88 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201205013
Abstract:
Several of the top ranked supercomputers are based on the hybrid architecture consisting of a large number of CPUs and GPUs. High performance has been obtained for problems with special structures, such as FFT-based imaging processing or N-body based particle calculations. However, for the class of problems described by partial differential equations (PDEs) discretized by finite difference (or other mesh based methods such as finite element) methods, obtaining even reasonably good performance on a CPU/GPU cluster is still a challenge. In this paper, we propose and test an hybrid algorithm which matches the architecture of the cluster. The scalability of the approach is implemented by a domain decomposition method, and the GPU performance is realized by using a smoothed aggregation based algebraic multigrid method. Incomplete factorization, which performs beautifully on CPU but poorly on GPU, is completely avoided in the approach. Numerical experiments are carried out by using up to 32 CPU/GPUs for solving PDE problems discretized by FDM with up to 32 millions unknowns.
-
2013,2(4):56-60 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201307010
Abstract:
Foot drop is the inability to voluntarily dorsiflex the ankle during the swing phase of gait and is usually caused by weakness and damages of the peroneal nerve. The consequences of the foot drop include the decreasing of gait quality, the limiting of mobility, the increasing of falling risk, and great increasing of energy expenditure during walking. Firstly biosignal sensors are used in the drop foot stimulator to detect foot movements. Then the surface drop foot stimulator produces a predefined stimulation profile to the peroneal nerve or tibialis anterial to elicit a dorsiflexion of the foot synchronized with the swing phase of gait to lift the foot. This paper reviewed the fundamentals and current researches of drop foot stimulators. Moreover, the development trends of the closed loop drop foot stimulator were also discussed in the paper.
-
2012,1(3):10-14 ,DOI: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201209002
Abstract:
Human action recognition acts as an important role in human machine interaction. This paper proposes a human body recognition method from depth image based on part size and position features. Random forest classifiers are trained with different parameters. Experimental results demonstrate the feasibility of proposed approach. Recognition accuracy is about 91% and the computation time is about 0.96 us per pixel.
-
Abstract:
Random Forests is an important ensemble learning method and it is widely used in data classification and nonparametric regression. In this paper, we review three main theoretical issues of random forests, i.e., the convergence theorem, the generalization error bound and the out-of-bag estimation. In the end, we present an improved Random Forests algorithm, which uses a feature weighting sampling method to sample a subset of features at each node in growing trees. The new method is suitable to solve classification problems of very high dimensional data.
-
Zheng Hongna, Zhu Yun, Wang LAN, Chen hui
Abstract:
In order to help the hearing loss children, we obtained hearing loss children’s fallible pronunciation texts and the confusing pronunciation text pairs form a good deal of hearing loss children’s audio pronunciation data. We designed a data-driven 3D talking head articulatory animation system, it was driven by the articulatory movements which were collected from a device called Electro-magnetic articulography (EMA) AG500, the system simulated Chinese articulation realistically. In that way, the hearing loss children can observe the speaker’s lips and tongue’s motions during the speaker pronouncing, which could help the hearing loss children train pronunciation and correct the fallible pronunciations. Finally, a perception test was applied to evaluate the system’s performance. The results showed that the 3D talking head system can animate both internal and external articulatory motions effectively. A modified CM model based synthesis method was used to generate the articulatory movements. The root mean square between the real articulatory movements and synthetic articulatory movements was used to measure the synthesis method, and an average value of RMS is 1.25 mm.
-
Rapid Detecting Method for Pseudosciaena Crocea Morphological Parameters Based on the Machine Vision
YU Xinjie,WU Xiongfei,Wang Jianping,CHEN Li,WANG Lei
2012,3(5):45-51, Doi: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201405006
Abstract:
Morphological parameter measurement of Pseudosciaena Crocea plays an important role in its genetic selection and quality improvement. In this paper, an automatic detecting system which can measure the Pseudosciaena Crocea morphological parameters such as weight, length and body width was developed based on the machine vision and weighing sensor technology. The system can automatically detect the external morphology parameters by the machine vision, and get weight parameters through the weighing sensor. The mean errors of dimensional measurement and weighting are 0.28% and 0.74% respectively, which shows that the developed system can completely meet the requirements of morphological parameter measurement for Pseudosciaena Crocea. It is a new effective method to the automatic detection of fish morphology parameters.
-
LIU Hengwei,LI Jianjun,XIE Xiaoyi,FANG Mou,WANG Li,HE Xiangming,OUYANG Minggao,LI Maogang
2015,4(1):51-59, Doi: 10.12146/j.issn.2095-3135.201501007
Abstract:
In this work the thermal behavior of the LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 cathode material for soft packed lithium-ion power batteries during charging and discharging at different C-rate were conducted using the ARC (accelerating rate calorimeter) to provide an adiabatic environment. The overall heat generated by the lithium-ion battery during use, is partly reversible and partly irreversible, due to entropy change and joule heating, respectively. It indicates that the heating generation of lithium-ion cell is decided by the C-rate of charge and discharge. The heat is smaller at low C-rate of charge and discharge. For example, the heating generation of battery increases 7.16℃ at 0.2C-rate and the entropy change heat is clearly embodied. The joule heating is more remarkable than the entropy change during charging and discharging at high C-rate. For instance, the heating generation of cell increased 25.63℃ at 1C-rate. The heat generation of charge is less than discharge at the same C-rate. The DC inter insistence of cell at the SOC (State of Charge) of 0 to 10% increases suddenly, so the heating generation power will reach its maximum in this period during discharge. It is valuable for the design of heat dissipation in lithium-ion battery thermal management.




 Virtual Special Issue
Virtual Special Issue
